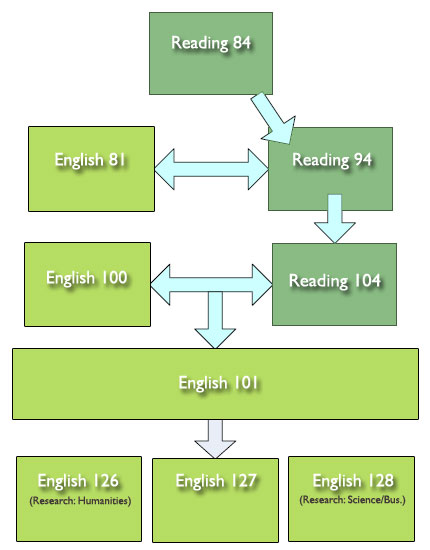
Reading 84
This course has four primary goals:
- To improve students reading vocabulary.
- To develop student reading comprehension.
- To increase student reading fluency and accuracy.
- To increase student enjoyment of reading.
Students will achieve these goals by developing the following
skills:
- Learning Greek and Latin word parts to develop vocabulary.
- Applying a variety of techniques to determine word
meaning.
- Identifying main ideas and supporting details.
- Utilizing word or structure cues to recognize writing
patterns that involve time order, examples, comparison
or contrast, and cause and effect.
- Utilizing pre-reading strategies to improve comprehension.
- Incorporating text marking strategies into reading
of a variety of materials.
English 81
To fulfill the requirements of English 81, the student
should be able to:
- Use the writing process in order to write clear,
well-organized paragraphs and build to short essays.
- Focus a topic for both a paragraph and a short essay,
develop ideas, organize ideas, write an introduction
and conclusion, and maintain unity (and coherence) in
their writing.
- Review sentence structure, mechanics, punctuation,
and spelling in order to write sentences that are clear
in meaning.
- Improve vocabulary.
- Improve skills in critical reading and writing by
examining a variety of texts that illustrate different
writing structures and themes. To demonstrate proficiency
in these course content outcomes, students will write
paragraphs and build to writing short essays, examine
assigned readings, participate in class discussions,
and take quizzes and tests.
Reading 94
This course has four primary goals:
- To improve student comprehension when reading a
variety materials.
- To provide students with study reading strategies
and techniques.
- To increase student reading speed and accuracy.
- To increase student enjoyment of reading.
Students will achieve these goals by developing the following
skills:
- Previewing, skimming, and scanning of reading material.
- Relating reading rate to purpose and text difficulty.
- Using a variety of techniques to determine word
meaning.
- Identifying main ideas and supporting details.
- Recognizing implied main ideas and the central points.
- Understanding relationships that involve addition
and time.
- Understanding relationships that involve examples,
comparison or contrast, and cause and effect.
- Distinguishing between fact and opinions.
- Making inferences.
- Understanding purpose and tone.
Student will demonstrate mastery of the skills listed
above by:
- Successful achievement on quizzes and tests.
- Successful achievement on reading drills and exercises.
- Answering written and oral comprehension questions.
- Cooperating in small and large group activities
in an active and collaborative manner.
- Active and meaningful participation in class discussion
and lecture.
Prerequisite = 2.0 or higher in Reading 84 or appropriate
COMPASS score.
English 100
To fulfill the requirement of English 100, students should
be able to demonstrate the following at the college level:
- Express their ideas clearly in writing;
- Organize paragraphs and expository essays;
- Develop greater facility with language;
- Improve their mechanics and usage.
Course content learning outcomes will be demonstrated
by:
- Writing a minimum of two expository paragraphs.
- Writing a minimum of one summary.
- Writing a minimum of three expository paper (for
instance, argument, process, comparison-contrast, etc.
or some combination of modes based on the assignment)
-- no secondary research in this level though)
- Revising papers extensively (revision of content:
ideas and analysis, structure, and development)
- Reviewing grammar and usage, sentence construction,
and mechanics as needed, and 6. reading and analyzing
short essays/articles/fiction as assigned by instructor
(from text, supplements, etc.).
Prerequisites = 2.0 in the previous reading and writing class in the sequence.
Reading 104
This course has four primary goals:
- To improve student comprehension of college reading
materials.
- To provide student with study reading strategies
and techniques.
- To increase student reading speed and accuracy.
- To enhance student critical reading skills.
The student will achieve these goals by developing the
following skills:
- Practicing the previewing, skimming, and scanning
of reading material.
- Setting reading goals for time and distance.
- Identifying main ideas and supporting details.
- Analyzing, interpreting, and synthesizing information
and ideas.
- Determining the author's purpose.
- Evaluating how effectively an author supports his
or her generalizations.
- Evaluating the evidence an author provides to support
a position.
- Distinguishing between fact and opinions.
- Using writing and textbook marking to monitor comprehension.
- Using writing and textbook marking to improve recall
and retention.
- Learning new words to expand vocabulary.
Student will demonstrate mastery of the skills listed
above by:
- Completion of reading assignments.
- Successful achievement on quizzes and tests.
- Answering written and oral comprehension questions.
- Applying various active-reading strategies to a
variety of texts.
- Cooperative and collaborative participation in small
and large group activities.
- Seeking agreement and solutions in small group discussions.
- Increasing speed while maintaining accuracy on reading
drills.
Prerequisite = a 2.0 in the previous reading and writing class in the sequence.
English 101
English 101 provides students with techniques and tools
for effective written communication, which include critical
thinking and reading; writing processes; and knowledge of
conventions. Specific assignments, texts, approaches, and
emphases will vary based on instructor. English 101 will
emphasize:
- Critical Thinking, Reading, and Writing: reading
and writing for inquiry, learning, thinking, and communicating;
understanding a writing assignment as a series of tasks,
including summarizing, evaluating, analyzing, and synthesizing
ideas; integrating their own ideas with those of others.
- Rhetorical Strategies: focusing on a purpose; responding
to the needs of different audiences; adopting appropriate
voice, diction, tone, and level of formality.
- Writing Process: recognizing the need for multiple
drafts to create and complete a successful text; developing
flexible strategies to generate, revise, edit, and proof-read;
understanding writing as a recursive process that enables
writers to change their drafts to improve form and content.
- Writing Conventions: selecting appropriate formats
for different kinds of purposes; practicing appropriate
means of documenting their work; using appropriate syntax,
grammar, punctuation, and spelling.
To demonstrate proficiency in the course content outcomes,
students will:
- Study and discuss rhetorical techniques.
- Critically read and discuss a variety of texts assigned
by the instructor.
- Submit three to five essays: three formal essays,
one of which will be documented, and two other formal
writing assignments, including (but not limited to)
summaries, reading responses, reflective essays, self-assessments,
essay exams, etc. By the end of the quarter, students
will produce a minimum of ten pages of formal essay
text.
- Revise written assignments to reflect rhetorical
knowledge and knowledge of conventions.
Prerequisite = 2.0 in the previous reading and writing class in the sequence
English 126 (Research: Humanities)
Students in ENGL 126 will pursue the following learning
outcomes:
- Critical reading: Read and evaluate a range of sources
in the disciplines of the humanities which may include
the study of literature, painting, music, film, etc.
at the discretion of the individual instructor; situate
sources in their historical, social, political, economic
and/or cultural contexts.
- Interpretive Strategies: Gain familiarity with and
practice using a variety of interpretive approaches,
such as attention to aesthetics, textual analysis, and
literary and cultural criticism, that are integral to
the study of humanities texts.
- Writing process: Practice writing as a recursive
process that includes topic selection and narrowing,
prewriting, research, planning, drafting, revising and
editing, and use tone, style, organization, content,
and argument to meet the needs and expectations of specific
writing contexts and audiences to produce writing that
is professional in format and appearance
- Academic arguments: Identify, evaluate, and be able
to develop the conventional components of an academic
argument, which may include research questions, issue
and/or claim (thesis or hypothesis); support (evidence
and explanation); warrant (assumptions, values, beliefs,
etc.); and engagement with multiple points of view.
Respectfully consider and engage the diverse perspectives
and intellectual contributions of others within the
classroom.
- Research tools and methodology: Gain familiarity
with a range of research tools and resources, including
library materials, electronic databases, the World Wide
Web, etc.; choose appropriate tools to find a wide and
diverse range of secondary sources, including scholarly
articles, and to evaluate critically those sources.
- Research writing and source integration: Learn and
apply the conventions of various common forms of research
writing, which may include annotated bibliography, research
proposal, and argument informed by research, among others.
Accurately and effectively incorporate and comment upon
references to a variety of sources; recognize the differences
among summary, paraphrase and direct quotation and when
to use each; cite sources according to documentation
style guides appropriate to specific disciplines within
the range of the humanities (MLA or CMS); understand
and avoid plagiarism.
- Diversity: Develop awareness of how social position
and geopolitical location can affect identity, perspective,
expression, and/or action. Evaluate how social, economic,
and/or political situation can affect the way ideas
are produced, distributed, and received.
To demonstrate proficiency in these course content outcomes,
students will:
- Produce a scholarly research paper (approximately
2000 words) that puts forth an academic argument supported
by reasoning and evidence based on research from primary
and secondary source materials
- Write other formal and informal writing assignments
totaling at least ten pages (2500-3000 words); these
may include shorter literary analysis essays, in-class
(timed) essay exams, annotated bibliographies, reading
responses, research progress reports, peer reviews,
reflective essays, self-assessments, etc.
Prerequisite = 2.0 and above in English 101.
English 127 (Research: Soc. Science)
Students in ENGL 127 will pursue the following learning
outcomes:
- Critical reading: Read and evaluate a range of sources
in the social sciences; situate sources in their historical,
social, political, economic and cultural contexts
- Writing process: Practice writing as a recursive
process that includes topic selection and narrowing,
prewriting planning, drafting, revising and editing,
and use tone, style, organization, content, and argument
to meet the needs and expectations of specific writing
contexts and audiences to produce writing that is professional
in substance, format, and appearance.
- Academic arguments: Identify, evaluate, and be able
to develop the conventional components of an academic
argument, including research question, claim, reasons,
support, warrants (assumptions, values, beliefs, etc.),
qualifiers, and engagement with multiple points of view.
Respectfully consider and engage the diverse perspectives
and intellectual contributions of others within the
classroom
- Research tools: Gain familiarity with a range of
research tools and resources, including library materials,
electronic databases, the World Wide Web, interviews,
etc.; choose appropriate tools to find a wide and diverse
range of secondary sources, including scholarly articles,
and critically evaluate those sources.
- Research writing: Learn and apply the conventions
of various common forms of research writing, which may
include annotated bibliography, research proposal, literature
review, research-based argument, among others.
- Source Integration: Accurately and effectively incorporate
and comment upon references to a variety of sources;
recognize the differences among summary, paraphrase,
and quotation, and when to use each; cite sources according
to APA (American Psychological Association) style; understand
and avoid plagiarism.
- Research methods: Recognize and analyze the various
qualitative and quantitative research methods employed
in the social sciences, such as survey, ethnography,
primary source analysis, observation, experiment, etc.
- Diversity: Develop awareness of how social position
and geopolitical location can affect identity, perspective,
expression, and/ or action. Evaluate how social, economic,
and or political power can affect the way ideas are
produced, distributed, and received.
The above objectives will be demonstrated
by a scholarly research paper that is at least ten pages
in length (2500-3000 words) and incorporates at least eight
diverse secondary sources; this paper should put forth an
academic argument that includes a thesis or hypothesis supported
by reasoning and evidence. Other formal and informal writing
assignments must total at least an additional ten pages
(2500-3000 words); these may include literature reviews,
research proposals, annotated bibliographies, reading responses,
research progress reports, peer reviews, reflective essays,
self-assessments, etc.
Prerequisite = 2.0 and above in English 101.
English 128 (Research Science/Business)
Building upon the skills, concepts presented in ENGL&
101, students in ENGL 128 will pursue the following learning
outcomes:
- Critical reading: Read and evaluate a range of sources
in the sciences, engineering, and business; situate
sources in their historical, social, political, economic
and/or cultural contexts.
- Writing process: Practice writing as a recursive
process that includes topic selection and narrowing,
prewriting, research, planning, drafting, revising and
editing, and use tone, style, organization, content,
and argument to meet the needs and expectations of specific
writing contexts and audiences to produce writing that
is professional in format and appearance.
- Academic arguments: Identify, evaluate, and be able
to develop the conventional components of an academic
argument, including research question, claim, reasons,
support, warrants (assumptions, values, beliefs, etc.),
qualifiers, and engagement with multiple points of view.
Respectfully consider and engage the diverse perspectives
and intellectual contributions of others within the
classroom.
- Research tools: Gain familiarity with a range of
research tools and resources, including library materials,
electronic databases, the World Wide Web, interviews,
etc.; choose appropriate tools to find a wide and diverse
range of secondary sources, including scholarly articles,
and to evaluate critically those sources.
- Research writing: Learn and apply the conventions
of various common forms of research writing, which may
include annotated bibliography, research proposal, literature
review, research-based argument, among others
- Source Integration: Accurately and effectively incorporate
and comment upon references to a variety of sources;
recognize the differences among summary, paraphrase
and direct quotation and when to use each; cite sources
according to documentation style guides appropriate
to specific disciplines within the range of humanities
(APA, MLA, CSE, CMS); understand and avoid plagiarism.
- Research methods: Recognize and analyze the various
qualitative and quantitative research methods employed
in the sciences, engineering, and business, such as
survey, interview, ethnography, primary source analysis,
observation, experiment, statistical analysis, among
others.
- Diversity: Develop awareness of how social position
and geopolitical location can affect identity, perspective,
expression, and/or action. Evaluate how social, economic,
and/or political power can affect the way ideas are
produced, distributed, and received.
To demonstrate proficiency, students will write a scholarly
research paper that is at least ten pages in length (2500-3000
words) and incorporates at least eight diverse secondary
sources; this paper should put forth an academic argument
that includes a thesis or hypothesis supported by reasoning
and evidence. Other formal and informal writing assignments
must total at least an additional ten pages (2500-3000 words);
these may include a literature review, research proposal,
annotated bibliography, reading responses, research progress
reports, peer reviews, reflective essays, self-assessments,
essay exams, etc.
Prerequisite = 2.0 and above in English 101.